What Does the Law of Constant Composition Mean
ElementAny one of the simplest chemical substances that cannot be decomposed in a chemical reaction or by any chemical means and are made up of atoms all having the same number of protons. In chemistry the law of constant composition also known as the law of definite proportions states that samples of a pure compound always contain the same elements in the same mass proportion.
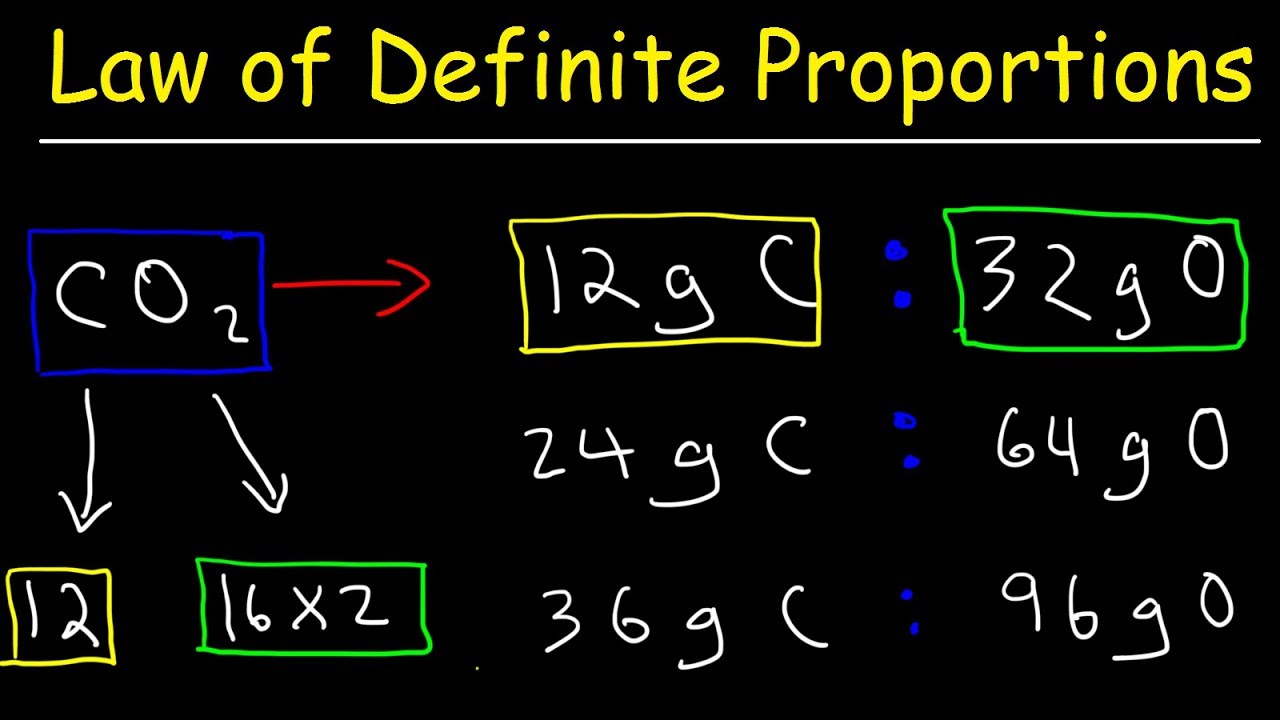
Law Of Definite Proportions Chemistry Practice Problems Chemical Fundamental Laws Youtube
Learn the basics about the law of constant composition and how to apply itThe law of constant composition states that in a given chemical compound all samp.

. The law of constant composition says that in any particular chemical compound all samples of that compound will be made up of the same elements in the same proportion or ratio. There is no definite formula for the composition of a mixture. For example pure water will always contain hydrogen and oxygen in a fixed mass ratio a gram.
This law describes that a given compound will always contain the same elements in the same proportions by mass. We can name this law as the law of definite proportions as well. Water H2O always consists of hydrogen and oxygen in a 19 mass ratio.
For example any water molecule is always made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom in a. The law of constant composition states that the chemical compounds consist of the elements which are present in a fixed ratio by their mass. The law of constant composition states that when elements are chemically combined they are always present in certain proportions by weight.
This implies that any pure sample of a compound no matter the source will always consist of the same elements that are present in the same ratio by mass. For example any water molecule is always made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom in a 21 ratio. This means that any given pure sample of the compound irrespective of its source will always contain the same kind of elements that are present in the same ratio by the mass.
In chemistry the law of constant composition states that the sample of a pure compound will always contain the same elements in the same proportion of the mass. Law of definite proportions - law stating that every pure substance always contains the same elements combined in the same proportions by weight law. In chemistry the law of definite proportion sometimes called Prousts law or law of constant composition states that a given chemical compound always contains its component elements in fixed ratio by mass and does not depend on its source and method of preparation.
The law of constant composition says that in any particular chemical compound all samples of that compound will be made up of the same elements in the same proportion or ratio. A molecule of water will always have two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom meaning that in a bottle of pure water the hydrogen to oxygen atom ratio will always be 2. Law Of Constant Composition Definition.
This is known as the law of constant composition. If you want to mix one spoonful of sugar with your tea you can. For example any water molecule is always made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom in a.
The law of constant composition says that in any particular chemical compound all samples of that compound will be made up of the same elements in the same proportion or ratio. The stoichiometry ratio for each ammonia molecule is 13. The law of constant composition states samples of a compound will always contain the same proportion of elements by mass.
Two or more elements when united to form a new substance do so in a constant and fixed proportion by weight. Law of constant composition - definition of Law of constant composition by The Free Dictionary. If you want to mix two you.
Law of definite compositionA law that states that chemical compounds are formed of constant and defined ratios of elements as determined by mass. Law of Constant Proportions. The law of constant proportions states that chemical compounds are made up of elements that are present in a fixed ratio by mass.
For example ammonia is composed of one atom of nitrogen and three atoms of hydrogen.

Law Of Constant Proportions Statement Explanation Exceptions Faqs

Difference Between Law Of Constant Composition And Law Of Multiple Proportions Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms

Law Of Constant Composition Properties Of Matter Chemistry Fuseschool Youtube

No comments for "What Does the Law of Constant Composition Mean"
Post a Comment